UAVs have become indispensable tools in the fields of land and soil management, as well as geography.
UAVs have become indispensable tools in the fields of land and soil management, as well as geography. They offer advanced solutions for monitoring, mapping, and analyzing various aspects of land and soil.
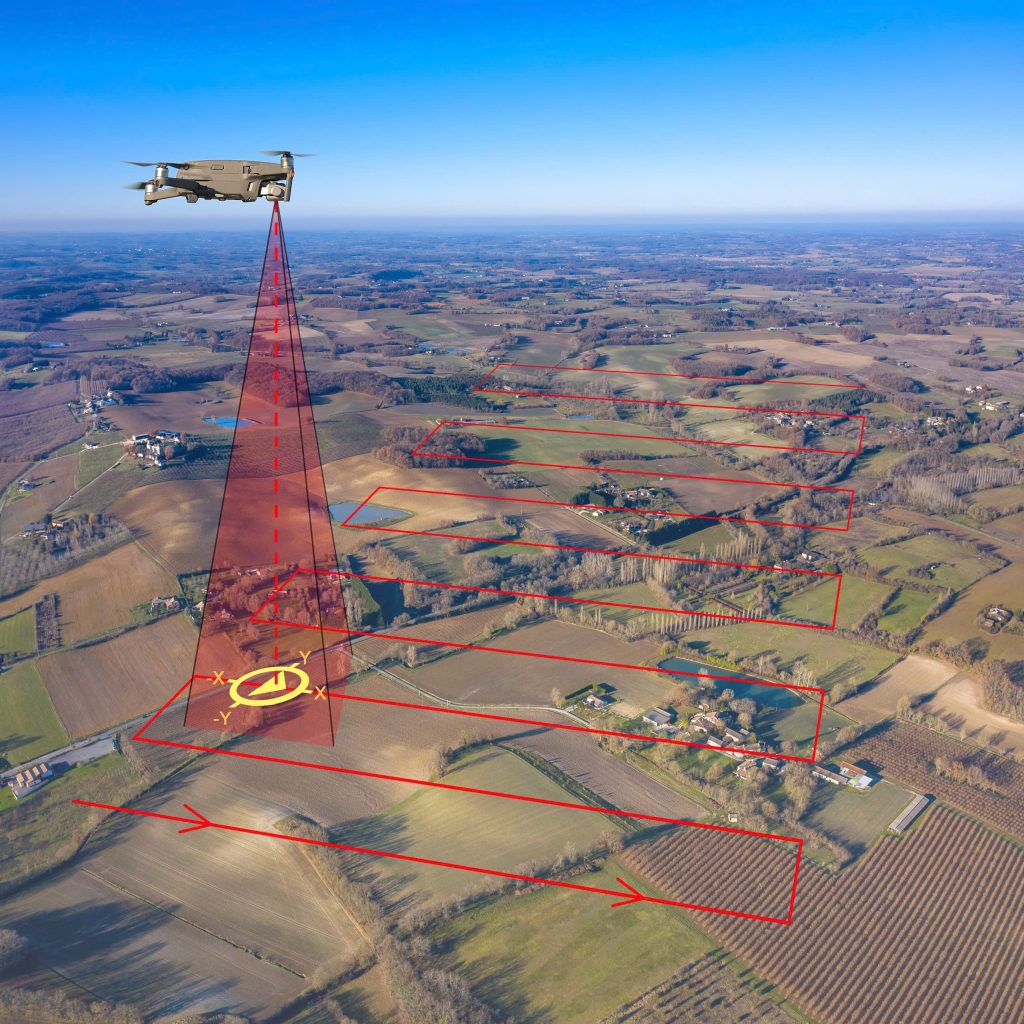
Land Mapping and Surveying
Soil Analysis and Management
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Integration
Environmental Monitoring
Disaster Management and Assessment
Land Use Planning
Biodiversity and Habitat Monitoring
Agricultural Planning and Management
Cost and Time Saving
Educational and Research Applications
In summary, UAVs offer significant advantages for land and soil management, as well as geographic studies. They provide high-resolution mapping, efficient data collection, and valuable insights for environmental monitoring, disaster management, and agricultural planning. Their ability to capture detailed aerial data makes them essential tools for improving land and soil management practices and advancing geographic research.

Copyright © 2024 CT UAV All Rights Reserved.