The increasing impacts of climate change have become more evident, particularly in rapidly urbanizing cities. Extreme weather events such as floods, droughts, and tropical storms are causing severe damage to human lives and infrastructure. Faced with these challenges, urban planners must leverage advanced technologies to build cities with greater resilience. Among these technologies, drone (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle – UAV) and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) have emerged as indispensable tools, enabling planners to design more sustainable and disaster-resistant urban environments.
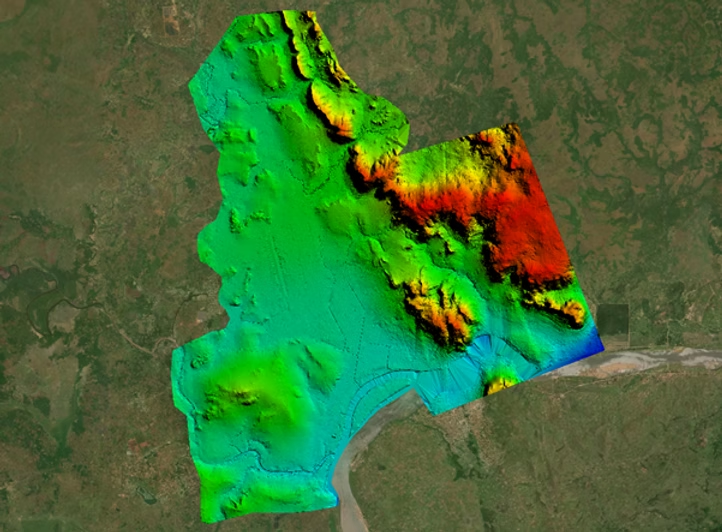
Understanding Drone and LiDAR Technology
Drone technology, particularly UAVs, has revolutionized various industries by providing high-resolution aerial imagery and facilitating rapid data collection. When integrated with LiDAR, a laser scanning technology that accurately measures distances, drones can generate highly detailed maps of terrain, built structures, and vegetation.
The use of drones and LiDAR in urban planning represents a significant breakthrough, allowing for large-scale data collection that supports precise decision-making. For instance, studies have shown that drone-based mapping can reduce project timelines by up to 75% compared to traditional methods, significantly enhancing cities’ responsiveness to natural disasters.
The Need for Sustainable Urban Planning
Many cities face unique vulnerabilities to climate change impacts. Limited financial resources, rapid urbanization, and underdeveloped infrastructure contribute to heightened disaster risks. Therefore, urban planning must integrate effective disaster risk reduction measures.
Flooding is one of the most pressing concerns in many regions. Research indicates that numerous informal settlements are located in high-risk flood zones. With the help of drones and LiDAR, urban planners can create highly accurate flood risk maps, identify hazardous areas, and design efficient drainage systems to protect local communities.
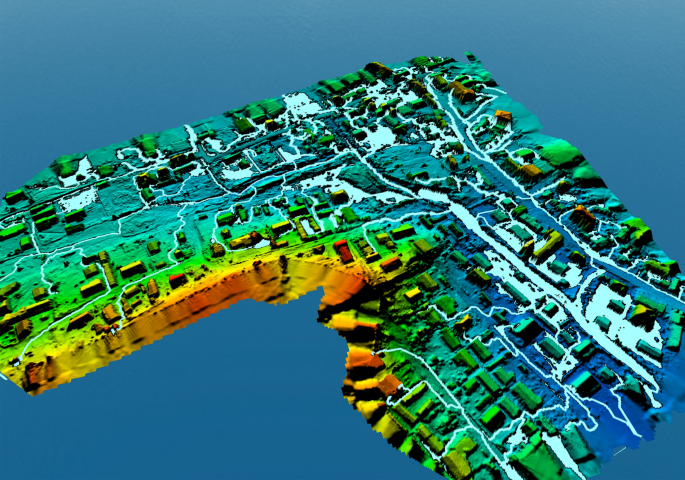
Enhancing Data Collection for Evidence-Based Planning
One of the most significant advantages of drone technology is its ability to collect data rapidly and efficiently compared to traditional surveying methods. Drones can access difficult-to-reach areas and generate detailed topographical maps within hours instead of weeks or months required by conventional land-based methods.
Meanwhile, LiDAR technology provides high-resolution terrain data, detecting even the smallest changes on the land surface. This information is critical for urban planners to understand water flow patterns, forecast flood risks, and develop mitigation strategies. For example, after implementing LiDAR data analysis, a city may reduce flood damage compensation claims by up to 40% within five years.
Monitoring Urban Development and Environmental Changes Over Time
As urban areas expand, environmental risks evolve. Continuous monitoring of urban growth is essential for assessing potential hazards. Drones can conduct regular aerial surveys, offering a dynamic and up-to-date overview of infrastructure changes and environmental transformations.
Data collected from these surveys help assess ecosystem health and pinpoint areas requiring intervention to mitigate climate change-related risks. For instance, by utilizing drone technology, urban planners have identified areas suitable for reforestation, contributing to flood control and carbon emission reduction.
Applications of Drone Technology in Urban Planning
Several cities have successfully employed UAV and LiDAR technology to enhance urban planning efforts. UAVs have been used to generate detailed maps for land management and disaster preparedness. By analyzing terrain data, planners have implemented strategies that significantly mitigate flood risks compared to previous approaches.
Drone-based surveys have also identified flood-prone areas, enabling governments to prioritize infrastructure investments. As a result, the frequency of recurring floods has been notably reduced, improving overall urban resilience.
Encouraging Community Engagement
The application of drones and LiDAR is not limited to technical use; it also fosters greater community awareness and engagement. High-quality aerial imagery enables planners to visualize data in a comprehensible manner for local residents.
These visual tools are crucial in discussions on land use planning, risk-prone areas, and necessary interventions. When communities understand the data, they can actively participate in planning processes. This transparency strengthens trust between municipal authorities and residents, ultimately contributing to more sustainable urban development.
Conclusion
The integration of drones and LiDAR in urban planning is a crucial step toward building climate-resilient cities. These technologies provide essential data and insights that inform strategic planning and disaster preparedness efforts.
Instead of relying on outdated methodologies, urban planners must embrace cutting-edge technology to turn challenges into opportunities, ensuring that cities develop sustainably and safely in the face of growing climate risks.
Cre: sUAS News
